
Curated with aloha by
Ted Mooney, P.E. RET

The authoritative public forum
for Metal Finishing 1989-2025

-----
Porosity Problems in Hard Chrome Plating
Q. A specification for Chromium plating (20-50 micrometer, without interface plating on Nickel alloys) requires Ferroxyl testing for porosity. I know this test more for detection of free iron on stainless steel to decide if passivation must be done or for testing of platings on low alloy steel. But does it work also in this case?
RICHARD BRUMMMATERIAL SCIENTIST - CELLE, GERMANY
October 31, 2021
A. Hi Richard,
Ferroxyl test is a pretty standard check for coating porosity. Some specs recommended it for Copper, Chrome, Nickel coatings on FERROUS substrates.
The whole idea of the Ferroxyl test is to penetrate through the cracks or pores and catch some Iron: small amount of Chlorides in the Ferroxyl solution convert Iron to an ion form (Fe2+) and it react with ferricyanide to create Prussian blue (Turnbull's blue as it was referred in past).
For my opinion it is useless to do the Ferroxyl test on Nickel based alloys, however I can be wrong. Try few drops of Ferroxyl on a piece of steel and on an uncoated piece of your alloy. If you see blue colour on the steel - your Ferroxyl solution works. If you do not see similar blue colour within a minute on your alloy - it will not work as a porosity test.
Good luck.
- Winnipeg, Canada
November 18, 2021
⇩ Related postings, oldest first ⇩
by Robert K. Guffie

on AbeBooks
(rarely)
or eBay
(rarely)
or Amazon
(affil links)
Q. We have been specifying Hard Chrome plating on some cylinders on wear surfaces. Since the Chromium deposition is quite porous, the substrate is getting corroded and bringing up the corrosion products to the surface. Can somebody suggest what can be done to seal the pores in Chrome deposit? Is there something similar to epoxy curing or do we have to resort to some other coating on the base metal before doing the chrome?
Mahesh [surname deleted for privacy by Editor]- Houston, Texas
2001
A. Eh, Mahesh, how thick is your hard chromium plating? If you're at
50 microns or more, you really shouldn't be having a corrosion problem. Chromium is cracked, yes, but it shouldn't be porous.
Decorative chromium plating is often plated over a thin layer of nickel to assist in the corrosion resistance. You might consider having this done. Should you insist on filling the pores, contact a firm that impregnates castings: the technology should be similar.
And finally, it's been my experience that HCl does a good job of attacking chromium plating, by enhancing the cracking in the layer. If you're using the hard chromium for hydrochloric acid service, perhaps something else should be considered.
Good luck!

Lee Gearhart
metallurgist - E. Aurora, New York
2001
Q. The coating at present is 0.0002" thick. The media used is hydraulic oil. Apparently the seals were not too good and some atmospheric moisture got inside coupled with "Sweating". These are the things causing the corrosion.
You say, cracks are present but the coating is not porous, but don't you think some ingression of moisture can take place towards the substrate thru the cracks? I am not very good in coating, forgive me if my question is something too obvious for an expert.
- Houston, Texas
2001
A. Five microns is too thin for "hard chrome" which is generally 10 times that thick. If you really are at 0.0002 inch, then you're either using "thin dense chrome" or "decorative chrome". The thin dense has less cracking, a nodular surface, and is usually used as plated. We usually use 0.0003 to 0.0005 thickness. Decorative chrome, found on bumpers, commonly has a nickel underlayer, whose barrier properties give the corrosion resistance.
Hard chrome, being thicker, has the advantage of great corrosion resistance, and the disadvantage of you're having to grind the plated surfaces after electroplating. The 50 micron thickness USUALLY means that any cracks don't go all the way from surface to substrate.
Hope this helps!
- East Aurora, New York
2001
Q. 0.002 thick chromium plating is scheduled for trials after 4th of July. Will post the outcome on this site. Thanks a lot for the advice.
Mahesh [returning]- Houston, Texas
2001
![]() The trials proved successful. Thanks a lot Lee for your valuable advise. Surprisingly there was not cost change for increased coating thickness. One problem down, thanks again.
The trials proved successful. Thanks a lot Lee for your valuable advise. Surprisingly there was not cost change for increased coating thickness. One problem down, thanks again.
- Houston, Texas
2001
Tip: This forum was established to build camaraderie among enthusiasts through sharing of tips, opinions, pics & personalities.
The curator & some of the readers who publicly share their info are unlikely to engage with posters who don't.
Q. I make a porosity ferroxyl test (potassium_ferricyanide
[affil links] + potassium ferrocyanide
⇦ this on
eBay
or
Amazon [affil links]
+ NaCl) on a hard chromium plated tube.
I have 2 results: one part have less porosity than the other
Could you give me the factors in the process of hard chromium which affect the porosity
Characteristics: hard chromium Thickness 20µm
DELPHI - TREMBLAY, FRANCE
2005
Tip: This forum was established to build camaraderie among enthusiasts through sharing of tips, opinions, pics & personalities.
The curator & some of the readers who publicly share their info are unlikely to engage with posters who don't.
A. At that thickness, hard chrome should easily pass your ferroxyl test. One possibility is excessively rough surface prior to plating. Others are improper mechanical finish after plating, or gas pitting due to poor agitation.

Jeffrey Holmes, CEF
Spartanburg, South Carolina
2005
by Artur Kutzelnigg
on AbeBooks
or Amazon
(affil links)
Q. How do you verify Porosity in Hard chrome plated components?
What is the Acceptance level of porosity and what are the methods to reduce / eliminate porosity in hard chrome plated parts?
- COIMBATORE, Tamil Nadu AND India
2005
A. For verification a 20/20 vision and good light to begin with. Then you can add magnifying lenses, microscopes of all kind, copper sulphate ⇦ this on eBay or Amazon [affil links] developer solution (just for ferrous materials), or what have you. About the porosity level of acceptance it is totally dependent on the use and applicable specifications (it would be different for an optical surface than for a car shock absorber or an airplane landing gear). To avoid them requires a long and thorough training course not an internet chat. G. Marrufo-Mexico
Guillermo MarrufoMonterrey, NL, Mexico
2005
by Weiner & Walmsley

on AbeBooks
(rarely)
or eBay
(sometimes)
or Amazon
(sometimes)
(affil links)
A. POROUS CHROMIUM DEPOSITS HAVE GREATER WEAR RESISTANCE OWING TO THEIR ABILITY TO RETAIN OIL.
TWO DISTINCT TYPE OF POROUS CHROMIUM ARE PRODUCED.
1.PIT TYPE USED FOR ALL TYPE OF ENGINES.
2.CHANNEL TYPE USED FOR AIR CRAFTS.
THE MOST WIDELY USED TECHNIQUE HOWEVER INVOLVE CHEMICAL OR ELECTROCHEMICAL ETCHING OF THE CHROMIUM DEPOSIT AFTER PLATING,THE ETCHED SURFACE IS FINISHED BY POLISHING OR LAPPING.
HOWEVER USING PROPRIETARY SOLUTIONS BY VARYING THE OPERATING CONDITIONS MICRO CRACKING IS ACHIEVED.
BEST DEPOSITS TYPICALLY MAY HAVE 800 TO 3000 CRACKS PER LINEAR INCH.
POROSITY FERROXYL TEST:- potassium_ferricyanide
[affil links],NACL
THE FERROXYL TEST IS USED TO EVALUATE THE POROSITY OF CHROMIUM DEPOSITS ON STEEL SUBSTRATES.AFTER BEING DIPPED INTO THE TEST SOLUTION A FILTER PAPER IS PLACED OVER DEPOSIT.THE FILTER PAPER IS REMOVED AFTER SOME TIME WASHED AND DRIED ANY PORES SHOW THEMSELVES AS BLUE SPOTS ON TEST PAPER.

Ajay Raina
Ludhiana, Punjab, India
2005
Q. We have a customer requesting AMS2460 test for porosity and corrosion resistance of our industrial hard chrome. We routinely perform ASTM B117 and have defended this test as superior and a more difficult test than AMS2460. Wondering if we are correct in this assessment.
William Gibsonplating shop employee - Morgantown, West Virginia, USA
April 7, 2011
A. Hi William,
This may be one where you will have to bite the bullet and live with your customer requirements. At the end of the day the customer has reasons for asking for a particular type of test. Come to that if the tests in AMS 2460 are not as severe as you already do then I would just do the less severe test, no need to set yourself up for potential failure!
The porosity test and the salt spray are different so it is difficult to say one or the other is harsher.
If you really want to stick to your testing regime then put together a technical report and submit it to your customer for consideration. If the argument is well reasoned I doubt they'll say no.
Aerospace - Yeovil, Somerset, UK
April 8, 2011
Q. We are required by a customer to do the "ferroxyl" test, as mentioned in FED QQ-C-320
now SAE AMS 2460, on 100% of a batch of chrome plated rods.
Both QQ-C-320B and SAE AMS 2460 describe this test as "destructive", that "renders actual parts not useable".
Is it so? If yes, we cannot do it on 100% of the parts! If yes, why?
Also, is it a really useful test to verify future corrosion resistance of the parts?
Quality Engineer - Reggio Emilia, ITALY
September 30, 2012
A. Are you sure that it is on 100% of parts and not 100% of lots? AMS 2460 allows porosity to be used as an acceptance test but also states that you can use test coupons "when it is not economically acceptable to perform destructive tests on actual parts" as long as the specimens are of the same generic class of alloy as the parts.
Scott Merritt- Eastman, Georgia, USA
October 3, 2012
Trouble with AMS2460 porosity test results
|
Q. We are now required to perform the porosity test per AMS2460 and after applying the potassium_ferricyanide
[affil links] (Ferroxyl), we keep having false positives for porosity. We call it false positives due to several coupons passing and through metallurgical guidance, the test panels that failed had no porosity under magnification; on the coupons/plated surface.  Claudine Meinhardt Chemist - San Antonio, Texas USA April 23, 2014 |
QUICKSTART |
A. The ferroxyl test is quite sensitive to iron. Either there is porosity in your plating, or there is iron from some other source on the surface. Try cleaning the panels before ferroxyl testing. You might wash with a soft brush and detergent, followed by rinsing with water which, by itself, is known not to react with ferroxyl.

Jeffrey Holmes, CEF
Spartanburg, South Carolina
May 5, 2014
![]() We have cleaned the panels with alkaline cleaner after plating. The alkaline cleaner is a new makeup with no contaminants. I will try basic detergent. Under cross-section, there is no porosity when the ferroxyl test shows a positive result. Thank you for your response.
We have cleaned the panels with alkaline cleaner after plating. The alkaline cleaner is a new makeup with no contaminants. I will try basic detergent. Under cross-section, there is no porosity when the ferroxyl test shows a positive result. Thank you for your response.

Claudine Meinhardt [returning]
- San Antonio, Texas, USA
May 6, 2014
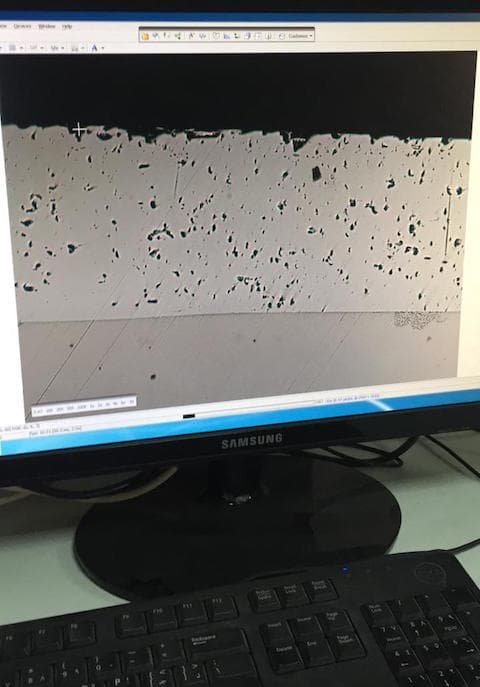
Q. I am working with a job shop that does hard chrome plating and nickel chrome plating on various components for the oil & gas and marine industry. Recently, we have done a test coupon in our bath which is HEEF 25 and the lab results of the cross section show high levels of porosity. We have never faced such an issue earlier. The current density we used is 30 A/dm2. The bath has less than 1 g/l of copper and iron content. PFA pictures for your better understanding that shows the defects based on observations through a microscope at 100X.
Dear team,
PFA picture of the microscopic view of our chrome plated sample in cross section. The top layer is hard chrome plated in HEEF 25 bath and the below parent material is of hardened AISI 4140. Please help me out in understanding the reason for this to occur as there were no surface defects observed when ground and polished.
I would greatly appreciate if anyone could let me know on what could be the reason for this. The surface was free of cracks and porosity as checked with dye penetrant.
Shop Employee - Dubai, United Arab Emirates
January 5, 2020
A. Hello Aravind Manoj Kumar,
In hard chrome plating a typical cause of porosity is an increase of trivalent chrome in the solution. Your TDS may have a way to check for this, but there should be a correlation between acid content and the specific gravity of the solution.
Another thing to look at is if you use a tin lead anode (typical), right after you plate a job check the anodes. If any are yellow that indicates they do not have a lead oxide film. This can cause a whole list of issues. If this is the case clean the anode bar and keep it clean, and if any are yellow give them a light brush and a lot of rinsing.
There are other causes for high porosity, but this is where I would start. Hope this helps!
- Sidney, New York, USA
January 8, 2020
A. Hi,
I should made a analysis by the trivalent chrome, it should not be higher than 3,5 g / litre. But for me the chrome deposit looks excellent. To the oil market I would recommend pulse plating deposit for the oil and gas buisness.
Regards

Anders Sundman
4th Generation Surface Engineering
Consultant - Arvika,
Sweden
January 16, 2020
Q. Hi William, thanks for your input.
I have checked the content of trivalent chrome but it is well below the limit as it was done in a new chemical bath. And even if the trivalent chrome was higher, don't you think that it would have shown on the surface as well, apart from the cross sectional view? Regarding clean anodes is something I will work on.
- Dubai, UAE
January 18, 2020
Q, A, or Comment on THIS thread -or- Start a NEW Thread
